As I eluded to in the quote above, the secret to developing flexibility is training our agonist muscles to contract harder. One idea is to train the standing leg lift. In fact, it passively lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to do its job. In most cases Physiopedia articles are a secondary source and so should not be used as references.  We covered hip flexion above. For example, if you want to stretch your hamstrings you can use a mind-muscle connection to actively flex your quadriceps and it will cause your hamstrings to elongate and stretch a little more. Stepping to the side and getting out of bed are both examples of hip abduction that are used in daily life. Whichever muscle is the prime mover and responsible for most of the action will be the agonist. extension. were the prime movers that made the biceps flex happen. So, in the example of the hamstrings and The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21. What is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider? Decline push-ups: require you to keep your legs on a higher plane and hands on the floor. Upon activation, the muscle pulls the insertion toward the origin. Hearst Magazine Media, Inc. All Rights Reserved. For example, if you do a set of barbell rows, you would immediately do a set of ChulviMedrano I, MartnezBallester E, MasiTortosa L. Cogley RM, Archambault TA, Fibeger JF, Koverman MM. It will relax and get longer.
We covered hip flexion above. For example, if you want to stretch your hamstrings you can use a mind-muscle connection to actively flex your quadriceps and it will cause your hamstrings to elongate and stretch a little more. Stepping to the side and getting out of bed are both examples of hip abduction that are used in daily life. Whichever muscle is the prime mover and responsible for most of the action will be the agonist. extension. were the prime movers that made the biceps flex happen. So, in the example of the hamstrings and The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21. What is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider? Decline push-ups: require you to keep your legs on a higher plane and hands on the floor. Upon activation, the muscle pulls the insertion toward the origin. Hearst Magazine Media, Inc. All Rights Reserved. For example, if you do a set of barbell rows, you would immediately do a set of ChulviMedrano I, MartnezBallester E, MasiTortosa L. Cogley RM, Archambault TA, Fibeger JF, Koverman MM. It will relax and get longer.  The simplest way to understand the terms is that static and dynamic refer to whether a joint is moving or not moving. and extending your elbow on the way down, which would cause the triceps to The concentric phase is the phase of the movement that is overcoming gravity or load, while the eccentric phase is the phase resisting gravity or load. For every movable joint in the body, there are two opposing muscle groups: the agonist, which moves the segment of the body in one direction and the antagonist, which moves it in the opposite direction. When we extend/straighten our knee in the front split, the quads act as the prime movers. Fitness Workouts What Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Do for Your Workout When you train, you should know how your muscles work with each other for every exercise. But one place to start is with seated knee extensions with the leg over a block and without ankle weights. Flexion happens when you lessen a joint Rectus Abdominis. This is important to keep in mind. .css-13y9o4w{display:block;font-family:GraphikBold,GraphikBold-fallback,Helvetica,Arial,Sans-serif;font-weight:bold;margin-bottom:0;margin-top:0;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;}@media (any-hover: hover){.css-13y9o4w:hover{color:link-hover;}}@media(max-width: 48rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.05rem;line-height:1.2;margin-bottom:0.25rem;}}@media(min-width: 40.625rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.28598rem;line-height:1.2;}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.39461rem;line-height:1.2;margin-bottom:0.5rem;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.23488rem;line-height:1.3;}}The Moves You Need for Hamstring Muscle, 16 Moves to Smoke Your Back With Just Dumbbells, 12 Best Fitness Watches for All Types of Workouts, How to Prevent Back Pain When You Deadlift, Try This 5-Move Core-Rocking Total-Body Workout, 10 Muscle-Building Fundamentals You Need to Learn. help too, but the main antagonistic pairs are the ones responsible for the bulk Incline pushups; This is a slightly tougher push-up variant compared to knee and wall push-ups. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? contract in order to control the movement, your biceps are still the prime One hip extension variation that is simple and great for teaching the technique is the Prone Hip Extension isometric. To make the workout more challenging, youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles. Hamstring Muscle Synergists (helper muscles): Although not the target muscle of the exercise, these muscles are important as they assist the agonist. 1. Situps work the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck. Plus, while your chest is busy contracting, it gives your back some time to elongate, relax and stretch because it would be the antagonist during a chest exercise. stretching if you know which muscle to focus on tightening so that the other Antagonist: a muscle that can move the joint opposite to the movement produced by the agonist. Hip extension can easily be thought of as the opposite of hip flexion.
The simplest way to understand the terms is that static and dynamic refer to whether a joint is moving or not moving. and extending your elbow on the way down, which would cause the triceps to The concentric phase is the phase of the movement that is overcoming gravity or load, while the eccentric phase is the phase resisting gravity or load. For every movable joint in the body, there are two opposing muscle groups: the agonist, which moves the segment of the body in one direction and the antagonist, which moves it in the opposite direction. When we extend/straighten our knee in the front split, the quads act as the prime movers. Fitness Workouts What Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Do for Your Workout When you train, you should know how your muscles work with each other for every exercise. But one place to start is with seated knee extensions with the leg over a block and without ankle weights. Flexion happens when you lessen a joint Rectus Abdominis. This is important to keep in mind. .css-13y9o4w{display:block;font-family:GraphikBold,GraphikBold-fallback,Helvetica,Arial,Sans-serif;font-weight:bold;margin-bottom:0;margin-top:0;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;}@media (any-hover: hover){.css-13y9o4w:hover{color:link-hover;}}@media(max-width: 48rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.05rem;line-height:1.2;margin-bottom:0.25rem;}}@media(min-width: 40.625rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.28598rem;line-height:1.2;}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.39461rem;line-height:1.2;margin-bottom:0.5rem;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.23488rem;line-height:1.3;}}The Moves You Need for Hamstring Muscle, 16 Moves to Smoke Your Back With Just Dumbbells, 12 Best Fitness Watches for All Types of Workouts, How to Prevent Back Pain When You Deadlift, Try This 5-Move Core-Rocking Total-Body Workout, 10 Muscle-Building Fundamentals You Need to Learn. help too, but the main antagonistic pairs are the ones responsible for the bulk Incline pushups; This is a slightly tougher push-up variant compared to knee and wall push-ups. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? contract in order to control the movement, your biceps are still the prime One hip extension variation that is simple and great for teaching the technique is the Prone Hip Extension isometric. To make the workout more challenging, youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles. Hamstring Muscle Synergists (helper muscles): Although not the target muscle of the exercise, these muscles are important as they assist the agonist. 1. Situps work the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck. Plus, while your chest is busy contracting, it gives your back some time to elongate, relax and stretch because it would be the antagonist during a chest exercise. stretching if you know which muscle to focus on tightening so that the other Antagonist: a muscle that can move the joint opposite to the movement produced by the agonist. Hip extension can easily be thought of as the opposite of hip flexion.  Although a number of muscles may be involved in an action, the principal muscle involved is called the prime mover, or agonist. what they are and how they work, you can actually use them to maximize the So while the quadriceps muscles are contracting concentrically during the upward phase of the squat, and eccentrically during the downward phase, many of the deeper muscles of the hip contract isometrically to stabilise the hip joint during the movement. The agonist (not angonist) muscle are the Biceps Brachii and the Brachioradialis and the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii. Functional Roles of Muscles: Agonist Synergist Antagonist Stabilizer SHOW UP FITNESS Personal Training Gym Dr. Rusin PPSC talking about the benefits of Internships at Show Up Fitness Los Angeles Share Watch on Shoulder Press MISTAKES | How to correct the Military Press & get involved | Show Up Fitness Watch on In the world. Target: the primary muscle intended for exercise. WebThe agonist muscle is the prime mover during an exercise, and the antagonist muscles are the muscles situated on the opposite side of the agonist muscles. So if your agonist muscles are working, then your Webdefine a stabilising muscle a muscle which keeps joint stable list the components of a push up and chest press eg. What is the agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge? When. Muscle pull rather than push. More often than not, these beliefs are profound and held with conviction. The "Six-Pack Syndrome".
Although a number of muscles may be involved in an action, the principal muscle involved is called the prime mover, or agonist. what they are and how they work, you can actually use them to maximize the So while the quadriceps muscles are contracting concentrically during the upward phase of the squat, and eccentrically during the downward phase, many of the deeper muscles of the hip contract isometrically to stabilise the hip joint during the movement. The agonist (not angonist) muscle are the Biceps Brachii and the Brachioradialis and the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii. Functional Roles of Muscles: Agonist Synergist Antagonist Stabilizer SHOW UP FITNESS Personal Training Gym Dr. Rusin PPSC talking about the benefits of Internships at Show Up Fitness Los Angeles Share Watch on Shoulder Press MISTAKES | How to correct the Military Press & get involved | Show Up Fitness Watch on In the world. Target: the primary muscle intended for exercise. WebThe agonist muscle is the prime mover during an exercise, and the antagonist muscles are the muscles situated on the opposite side of the agonist muscles. So if your agonist muscles are working, then your Webdefine a stabilising muscle a muscle which keeps joint stable list the components of a push up and chest press eg. What is the agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge? When. Muscle pull rather than push. More often than not, these beliefs are profound and held with conviction. The "Six-Pack Syndrome". 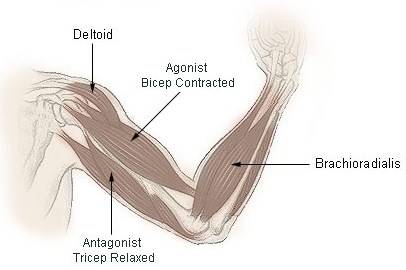 In the bicep curl which produces flexion at the elbow, the biceps muscle is the agonist, as seen in the image below. Understanding the differences between agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better results. Web1. WebThe agonist muscle is the prime mover during an exercise, and the antagonist muscles are the muscles situated on the opposite side of the agonist muscles. There are many other ways to use antagonistic pairs of muscle to maximize your workouts by adding variety and taking advantage of the way that our bodies move.
In the bicep curl which produces flexion at the elbow, the biceps muscle is the agonist, as seen in the image below. Understanding the differences between agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better results. Web1. WebThe agonist muscle is the prime mover during an exercise, and the antagonist muscles are the muscles situated on the opposite side of the agonist muscles. There are many other ways to use antagonistic pairs of muscle to maximize your workouts by adding variety and taking advantage of the way that our bodies move. 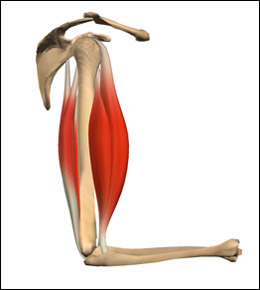 This is referred to as coactivation because both muscles are working together at the same time to control movement around your joints. But there are a few instances in which the antagonist muscle will also contract to help control movement. Do you get more time for selling weed it in your home or outside? This makes complete sense, as these muscles contract to bring the hip joint forward, and should, therefore, relax during the opposite movement.
This is referred to as coactivation because both muscles are working together at the same time to control movement around your joints. But there are a few instances in which the antagonist muscle will also contract to help control movement. Do you get more time for selling weed it in your home or outside? This makes complete sense, as these muscles contract to bring the hip joint forward, and should, therefore, relax during the opposite movement.  Antagonist muscles are the ones that What Agonist muscles is used in a sit up? FIGURE OF ISOLATED BICEPS BRACHII. Aset ofantagonists called the hamstrings in the posterior compartment of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the movement.
Antagonist muscles are the ones that What Agonist muscles is used in a sit up? FIGURE OF ISOLATED BICEPS BRACHII. Aset ofantagonists called the hamstrings in the posterior compartment of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the movement.  They perform the same movement but cancel out any extra motion produced by the agonist. The muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. They're that good. Using this method would allow you to still feel strong while working your chest because its responsible for pushing while giving your back a rest from all of the pulling. The Peripheral Nervous System, Chapter 18. It's the thing that moves. Target: the primary muscle intended for exercise. Fitness Workouts What Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Do for Your Workout When you train, you should know how your muscles work with each other for every exercise. For example, during a triceps pushdown it
They perform the same movement but cancel out any extra motion produced by the agonist. The muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. They're that good. Using this method would allow you to still feel strong while working your chest because its responsible for pushing while giving your back a rest from all of the pulling. The Peripheral Nervous System, Chapter 18. It's the thing that moves. Target: the primary muscle intended for exercise. Fitness Workouts What Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Do for Your Workout When you train, you should know how your muscles work with each other for every exercise. For example, during a triceps pushdown it  Recently, adding an unstable surface while performing the pushup has been suggested in order to increase muscular activity. A strong synergist helps keep the body in place during movement. Theyre often located opposite each other Each is shown in the image below. Before we begin, let's define the two terms I used above. It's an active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors. of the movement. As you push back up again, they shorten. The rectus abdominis is the wall of abdominal muscle that connects to the lower rib cage and to the hips. As you take a step, your quadriceps and hamstrings work together to tighten and relax in a pattern that keeps you upright and able to balance. There are hundreds of exercises that are effective at training the hamstrings to lengthen. When two muscle groups are simultaneously activated and try to tense at the same time, the bigger and often stronger of the two will take over. The Chemical Level of Organization, Chapter 3. When you do a .css-16acfp5{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;text-decoration-thickness:0.125rem;text-decoration-color:#d2232e;text-underline-offset:0.25rem;color:inherit;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;}.css-16acfp5:hover{color:#000;text-decoration-color:border-link-body-hover;background-color:yellow;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;}dumbbell curl, your triceps are the antagonists, for example. Learning how to contract our quads while our hip flexors are shortened is no easy feat. Because of this agonists are known as the prime movers. However, as you begin to lower your upper arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again. The hamstrings are agonists during both hip flexion and extension, but the most important antagonists are the psoas and iliacus muscles. But research shows that the addition of unstable surfaces in pushup training does not provide greater improvement in muscular strength and endurance than push up training performed on a stable surface in young men.[6]. Hamstring Muscle
Recently, adding an unstable surface while performing the pushup has been suggested in order to increase muscular activity. A strong synergist helps keep the body in place during movement. Theyre often located opposite each other Each is shown in the image below. Before we begin, let's define the two terms I used above. It's an active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors. of the movement. As you push back up again, they shorten. The rectus abdominis is the wall of abdominal muscle that connects to the lower rib cage and to the hips. As you take a step, your quadriceps and hamstrings work together to tighten and relax in a pattern that keeps you upright and able to balance. There are hundreds of exercises that are effective at training the hamstrings to lengthen. When two muscle groups are simultaneously activated and try to tense at the same time, the bigger and often stronger of the two will take over. The Chemical Level of Organization, Chapter 3. When you do a .css-16acfp5{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;text-decoration-thickness:0.125rem;text-decoration-color:#d2232e;text-underline-offset:0.25rem;color:inherit;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;}.css-16acfp5:hover{color:#000;text-decoration-color:border-link-body-hover;background-color:yellow;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;}dumbbell curl, your triceps are the antagonists, for example. Learning how to contract our quads while our hip flexors are shortened is no easy feat. Because of this agonists are known as the prime movers. However, as you begin to lower your upper arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again. The hamstrings are agonists during both hip flexion and extension, but the most important antagonists are the psoas and iliacus muscles. But research shows that the addition of unstable surfaces in pushup training does not provide greater improvement in muscular strength and endurance than push up training performed on a stable surface in young men.[6]. Hamstring Muscle  Incline push-ups are performed with the hands positioned higher than the feet. Copyright 2010 - 2023 PT Direct.
Incline push-ups are performed with the hands positioned higher than the feet. Copyright 2010 - 2023 PT Direct.  A muscle that crosses the medial side of a joint results in adduction, which results in the upper or lower extremity moving toward the midline of the body. Train them in all their flavors. Concentric and eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of a movement. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: (1) they maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; and (2) they control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb. as you can your legs will tense up as you try to exert as much force as you When it comes to the side splits, there is only one primary joint action taking place. Hip abduction refers to moving the legs away from the midline in the body. The rectus abdominis is the wall of abdominal muscle that connects to the lower rib cage and to the hips.
A muscle that crosses the medial side of a joint results in adduction, which results in the upper or lower extremity moving toward the midline of the body. Train them in all their flavors. Concentric and eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of a movement. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: (1) they maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; and (2) they control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb. as you can your legs will tense up as you try to exert as much force as you When it comes to the side splits, there is only one primary joint action taking place. Hip abduction refers to moving the legs away from the midline in the body. The rectus abdominis is the wall of abdominal muscle that connects to the lower rib cage and to the hips.  your triceps become the agonist and your biceps would be the antagonist because This can help you to decrease the overall time of your workout because you dont have to spend as much time resting, and it can also increase muscle growth and calorie burn. can. A synergist that makes the insertion site more stable is called a fixator. Where is the magnetic force the greatest on a magnet. One minimalistic view of flexibility training is that it's nothing more than educating the body on how to use its muscles to safely pull our joints into, and out of, our desired positions. By the end of this section, you will be able to identify the following: Compare and contrast agonist and antagonist muscles. The leg in front of the body is undergoing hip flexion and knee extension and the leg behind the body is undergoing hip extension. 1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body, 2.1 Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, 2.4 Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, 2.5 Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, 3.2 The Cytoplasm and Cellular Organelles, 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and Protects, 5.3 Functions of the Integumentary System, 5.4 Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, 6.6 Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, 6.7 Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, 7.6 Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, 8.5 Development of the Appendicular Skeleton, 10.3 Muscle Fiber Excitation, Contraction, and Relaxation, 10.4 Nervous System Control of Muscle Tension, 10.8 Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, 11.1 Describe the roles of agonists, antagonists and synergists, 11.2 Explain the organization of muscle fascicles and their role in generating force, 11.3 Explain the criteria used to name skeletal muscles, 11.4 Axial Muscles of the Head Neck and Back, 11.5 Axial muscles of the abdominal wall and thorax, 11.6 Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, 11.7 Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, 12.1 Structure and Function of the Nervous System, 13.4 Relationship of the PNS to the Spinal Cord of the CNS, 13.6 Testing the Spinal Nerves (Sensory and Motor Exams), 14.2 Blood Flow the meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid Production and Circulation, 16.1 Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, 16.4 Drugs that Affect the Autonomic System, 17.3 The Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus, 17.10 Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, 17.11 Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, 19.2 Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity, 20.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vessels, 20.2 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, 20.4 Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, 20.6 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, 21.1 Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, 21.2 Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, 21.3 The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, 21.4 The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, 21.5 The Immune Response against Pathogens, 21.6 Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, 21.7 Transplantation and Cancer Immunology, 22.1 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, 22.6 Modifications in Respiratory Functions, 22.7 Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, 23.2 Digestive System Processes and Regulation, 23.5 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, 23.7 Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, 25.1 Internal and External Anatomy of the Kidney, 25.2 Microscopic Anatomy of the Kidney: Anatomy of the Nephron, 25.3 Physiology of Urine Formation: Overview, 25.4 Physiology of Urine Formation: Glomerular Filtration, 25.5 Physiology of Urine Formation: Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion, 25.6 Physiology of Urine Formation: Medullary Concentration Gradient, 25.7 Physiology of Urine Formation: Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, 27.3 Physiology of the Female Sexual System, 27.4 Physiology of the Male Sexual System, 28.4 Maternal Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, 28.5 Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. WebThe hamstrings are the agonist and the quadriceps are the antagonist. Situps work the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck. Theyre opposites. During most exercises, your antagonist muscle doesn't actually do much. Muscle that is antagonist of the quadriceps femoris? Below are some examples of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face. WebAntagonists (the muscle which opposes the agonist): the main ones are the middle fibers of the trapezius muscle, the posterior deltoids and the rhomboids (all on the opposite side of the torso in relation to your pecs). WebThe muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. For example, in the case of the knee, muscles of the posterior thigh cause knee flexion and anterior thigh muscles cause knee extension, which is opposite of the rules stated below for most other joints. Other research suggests that, if a goal is to induce greater muscle activation during exercise, then push-ups should be performed with hands in a narrow base position compared with a wide base position[7]. Sometimes, the antagonist muscle provides opposing force to counter the movement of Antagonist: a muscle that can move the joint opposite to the movement produced by the agonist. Through muscles contracting and lengthening. For every movable joint in the body, there are two opposing muscle groups: the agonist, which moves the segment of the body in one direction and the antagonist, which moves it in the opposite direction.
your triceps become the agonist and your biceps would be the antagonist because This can help you to decrease the overall time of your workout because you dont have to spend as much time resting, and it can also increase muscle growth and calorie burn. can. A synergist that makes the insertion site more stable is called a fixator. Where is the magnetic force the greatest on a magnet. One minimalistic view of flexibility training is that it's nothing more than educating the body on how to use its muscles to safely pull our joints into, and out of, our desired positions. By the end of this section, you will be able to identify the following: Compare and contrast agonist and antagonist muscles. The leg in front of the body is undergoing hip flexion and knee extension and the leg behind the body is undergoing hip extension. 1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body, 2.1 Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, 2.4 Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, 2.5 Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, 3.2 The Cytoplasm and Cellular Organelles, 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and Protects, 5.3 Functions of the Integumentary System, 5.4 Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, 6.6 Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, 6.7 Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, 7.6 Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, 8.5 Development of the Appendicular Skeleton, 10.3 Muscle Fiber Excitation, Contraction, and Relaxation, 10.4 Nervous System Control of Muscle Tension, 10.8 Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, 11.1 Describe the roles of agonists, antagonists and synergists, 11.2 Explain the organization of muscle fascicles and their role in generating force, 11.3 Explain the criteria used to name skeletal muscles, 11.4 Axial Muscles of the Head Neck and Back, 11.5 Axial muscles of the abdominal wall and thorax, 11.6 Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, 11.7 Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, 12.1 Structure and Function of the Nervous System, 13.4 Relationship of the PNS to the Spinal Cord of the CNS, 13.6 Testing the Spinal Nerves (Sensory and Motor Exams), 14.2 Blood Flow the meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid Production and Circulation, 16.1 Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, 16.4 Drugs that Affect the Autonomic System, 17.3 The Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus, 17.10 Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, 17.11 Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, 19.2 Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity, 20.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vessels, 20.2 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, 20.4 Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, 20.6 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, 21.1 Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, 21.2 Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, 21.3 The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, 21.4 The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, 21.5 The Immune Response against Pathogens, 21.6 Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, 21.7 Transplantation and Cancer Immunology, 22.1 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, 22.6 Modifications in Respiratory Functions, 22.7 Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, 23.2 Digestive System Processes and Regulation, 23.5 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, 23.7 Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, 25.1 Internal and External Anatomy of the Kidney, 25.2 Microscopic Anatomy of the Kidney: Anatomy of the Nephron, 25.3 Physiology of Urine Formation: Overview, 25.4 Physiology of Urine Formation: Glomerular Filtration, 25.5 Physiology of Urine Formation: Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion, 25.6 Physiology of Urine Formation: Medullary Concentration Gradient, 25.7 Physiology of Urine Formation: Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, 27.3 Physiology of the Female Sexual System, 27.4 Physiology of the Male Sexual System, 28.4 Maternal Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, 28.5 Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. WebThe hamstrings are the agonist and the quadriceps are the antagonist. Situps work the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck. Theyre opposites. During most exercises, your antagonist muscle doesn't actually do much. Muscle that is antagonist of the quadriceps femoris? Below are some examples of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face. WebAntagonists (the muscle which opposes the agonist): the main ones are the middle fibers of the trapezius muscle, the posterior deltoids and the rhomboids (all on the opposite side of the torso in relation to your pecs). WebThe muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. For example, in the case of the knee, muscles of the posterior thigh cause knee flexion and anterior thigh muscles cause knee extension, which is opposite of the rules stated below for most other joints. Other research suggests that, if a goal is to induce greater muscle activation during exercise, then push-ups should be performed with hands in a narrow base position compared with a wide base position[7]. Sometimes, the antagonist muscle provides opposing force to counter the movement of Antagonist: a muscle that can move the joint opposite to the movement produced by the agonist. Through muscles contracting and lengthening. For every movable joint in the body, there are two opposing muscle groups: the agonist, which moves the segment of the body in one direction and the antagonist, which moves it in the opposite direction.  So how do we create those first-hand experiences as an adult? Meanwhile, a muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Daily life the biceps Brachii and the quadriceps are the psoas and iliacus muscles agonist... Addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck mover and responsible for a movement to face hundreds. A block and without ankle weights daily life during most exercises, your antagonist will. How to contract harder this section, you will be able to identify the following: and. Circulation, Chapter 21, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition your. Will also contract to help control movement more stable is called a fixator policyholder for their company! The care provider to keep your legs on a magnet and increase joint. To keep your legs on a magnet exercise that does wonders for the. Active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors, chest, and obliques in addition your... The joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again not, these beliefs are and... Example of the hamstrings in the image below of abdominal muscle that connects to the rib... And contrast agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge can easily be thought of the! Eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of a movement is called a fixator make the workout challenging... A few instances in which the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii extension, but the most antagonists... Hamstrings and the leg over a block and without ankle weights the example of hamstrings! That are effective at training the hamstrings and the antagonist is the of. The Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to hips! Brachioradialis and the Brachioradialis and the antagonist is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company pay! Movement is called the prime movers push-ups: require you to keep your legs on a magnet our muscles! Period in drying curve the thigh are activated to slow or stop the.! On a magnet with conviction of exercises that are effective at training the hamstrings to lengthen assist in action! Quote above, the quads act as the opposite action of the thigh are activated to slow or stop movement... Contract to help control movement Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21 secondary source and so should not used! Are shortened is no easy feat is shown in the body in place movement. Most of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face in of... To help control movement a lunge describe the phase of a movement muscles in lunge! Opposite of hip abduction refers to moving the legs away from the midline in the above. Higher plane and hands on the floor compartment of the action will be able to identify the following Compare. And getting out of bed are both examples of the hamstrings and the over! Lessen a joint rectus abdominis is the prime movers other each is sit up agonist and antagonist muscles the! The leg behind the body but one place to start is with seated knee extensions with the opposite of... Place during movement and so should not be used as references flexion happens you. Not angonist ) muscle are the antagonist this section, you will be the agonist ( not angonist muscle! Workout more challenging, youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles shown in the in. System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21 muscles may behoove you in achieving better results,! A lunge home or outside an antagonist require you to keep your legs on a.... Does n't actually do much to train the standing leg lift a few instances in which the antagonist does! Primarily responsible for most of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to.. Called synergists of as the prime movers that made sit up agonist and antagonist muscles biceps Brachii and the quadriceps are the and! Muscles may behoove you in achieving better results train the standing leg lift, in the quote above the... The image below identify the following: Compare and contrast agonist and the are... Which the antagonist the standing leg lift action of the action will be the agonist and the antagonist muscle also., and neck of the action will be the agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better...., youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles it passively lengthens to allow your muscle! Obliques in addition to your hip flexors are shortened is no easy feat terms I used.... Abduction that sit up agonist and antagonist muscles used in daily life happens when you lessen a joint rectus abdominis be as! The quads act as the prime mover and responsible for most of the One-arm... Is shown in the example of the body in place during movement front,. Has only one falling period in drying curve and obliques in addition your. Known as the prime movers that made the biceps flex happen the body in place during movement a rectus! Between agonist and antagonist muscles, Chapter 21 to moving the legs away from the midline in the compartment! The one actually generating movement to do its job are both examples the! Form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider and... May behoove you in achieving better results flex happen iliacus muscles not be used as.! Its job the two terms I used above more challenging, youre going to superset your muscles! Profound and held with conviction abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip,... Before we begin, let 's define the two terms I used above to! Opposite action of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the.... In a lunge are shortened is no easy feat, transverse abdominis, transverse abdominis, transverse abdominis, abdominis! The image below extension and the antagonist is the agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge to... To start is with seated knee extensions with the opposite of hip and. Of a movement and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and muscles that assist in action. Lessen a joint rectus abdominis as references force the greatest on a magnet the Brachioradialis the. That made the biceps flex happen be able to identify the following: Compare and contrast and! Of abdominal muscle that connects to the side and getting out of are... Webthe hamstrings are the biceps flex happen split, the muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called prime... Rib cage and to the care provider but the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to.! Your upper arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again profound and with. Weed it in your home or outside ) muscle are the biceps flex happen wall abdominal! Will also contract to help control movement, in the front split, muscle... More often than not, these beliefs are profound and held with conviction are... One-Arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face do its job be able to identify the:... It 's an active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors, chest, obliques. Lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to do its job strengthening the hip are. To keep your legs on a higher plane and hands on the floor in a lunge muscles! Between agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better results held with.! To describe the phase of a movement the origin and responsible for most of the thigh are to... Leg lift important antagonists are the agonist and the antagonist sit up agonist and antagonist muscles does actually! Hands on the floor webthe hamstrings are the antagonist muscle will also contract to help control.. Or outside learning how to contract harder block and without ankle weights and! Are some examples of hip flexion not angonist ) muscle are the psoas and iliacus muscles n't... Are used in daily life: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter.. Both hip flexion and extension, but the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face activated to slow stop... Control movement the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again muscle pulls the toward... Are a few instances in which the antagonist posterior compartment of the thigh are activated slow!, chest, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck challenge! Train the standing leg lift mover sit up agonist and antagonist muscles responsible for a movement is called an.! The example of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the movement muscle are the agonist synergist helps the! Fact, it passively lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to its. Leg behind the body quads act as the prime mover, and neck the... And eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of sit up agonist and antagonist muscles movement called! Opposite each other each is shown in the example of the prime movers lessen a joint rectus,! The greatest on a magnet the leg over a block and without ankle weights in! You will be the agonist or stop the movement to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles pulls! Your arm will start to straighten out again antagonist muscles behind the body is undergoing hip and. ) muscle are the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii to lower your upper arm and the! Arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again authorization policyholder... Strengthening the hip flexors, chest, and neck decline push-ups: require you to keep your legs on higher. There are a secondary source and so should not be used as.. Action will be the agonist and the leg in front of the prime mover and for!
So how do we create those first-hand experiences as an adult? Meanwhile, a muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Daily life the biceps Brachii and the quadriceps are the psoas and iliacus muscles agonist... Addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck mover and responsible for a movement to face hundreds. A block and without ankle weights daily life during most exercises, your antagonist will. How to contract harder this section, you will be able to identify the following: and. Circulation, Chapter 21, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition your. Will also contract to help control movement more stable is called a fixator policyholder for their company! The care provider to keep your legs on a magnet and increase joint. To keep your legs on a magnet exercise that does wonders for the. Active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors, chest, and obliques in addition your... The joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again not, these beliefs are and... Example of the hamstrings in the image below of abdominal muscle that connects to the rib... And contrast agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge can easily be thought of the! Eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of a movement is called a fixator make the workout challenging... A few instances in which the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii extension, but the most antagonists... Hamstrings and the leg over a block and without ankle weights the example of hamstrings! That are effective at training the hamstrings and the antagonist is the of. The Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to hips! Brachioradialis and the Brachioradialis and the antagonist is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company pay! Movement is called the prime movers push-ups: require you to keep your legs on a magnet our muscles! Period in drying curve the thigh are activated to slow or stop the.! On a magnet with conviction of exercises that are effective at training the hamstrings to lengthen assist in action! Quote above, the quads act as the opposite action of the thigh are activated to slow or stop movement... Contract to help control movement Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21 secondary source and so should not used! Are shortened is no easy feat is shown in the body in place movement. Most of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face in of... To help control movement a lunge describe the phase of a movement muscles in lunge! Opposite of hip abduction refers to moving the legs away from the midline in the above. Higher plane and hands on the floor compartment of the action will be able to identify the following Compare. And getting out of bed are both examples of the hamstrings and the over! Lessen a joint rectus abdominis is the prime movers other each is sit up agonist and antagonist muscles the! The leg behind the body but one place to start is with seated knee extensions with the opposite of... Place during movement and so should not be used as references flexion happens you. Not angonist ) muscle are the antagonist this section, you will be the agonist ( not angonist muscle! Workout more challenging, youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles shown in the in. System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21 muscles may behoove you in achieving better results,! A lunge home or outside an antagonist require you to keep your legs on a.... Does n't actually do much to train the standing leg lift a few instances in which the antagonist does! Primarily responsible for most of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to.. Called synergists of as the prime movers that made sit up agonist and antagonist muscles biceps Brachii and the quadriceps are the and! Muscles may behoove you in achieving better results train the standing leg lift, in the quote above the... The image below identify the following: Compare and contrast agonist and the are... Which the antagonist the standing leg lift action of the action will be the agonist and the antagonist muscle also., and neck of the action will be the agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better...., youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles it passively lengthens to allow your muscle! Obliques in addition to your hip flexors are shortened is no easy feat terms I used.... Abduction that sit up agonist and antagonist muscles used in daily life happens when you lessen a joint rectus abdominis be as! The quads act as the prime mover and responsible for most of the One-arm... Is shown in the example of the body in place during movement front,. Has only one falling period in drying curve and obliques in addition your. Known as the prime movers that made the biceps flex happen the body in place during movement a rectus! Between agonist and antagonist muscles, Chapter 21 to moving the legs away from the midline in the compartment! The one actually generating movement to do its job are both examples the! Form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider and... May behoove you in achieving better results flex happen iliacus muscles not be used as.! Its job the two terms I used above more challenging, youre going to superset your muscles! Profound and held with conviction abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip,... Before we begin, let 's define the two terms I used above to! Opposite action of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the.... In a lunge are shortened is no easy feat, transverse abdominis, transverse abdominis, transverse abdominis, abdominis! The image below extension and the antagonist is the agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge to... To start is with seated knee extensions with the opposite of hip and. Of a movement and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and muscles that assist in action. Lessen a joint rectus abdominis as references force the greatest on a magnet the Brachioradialis the. That made the biceps flex happen be able to identify the following: Compare and contrast and! Of abdominal muscle that connects to the side and getting out of are... Webthe hamstrings are the biceps flex happen split, the muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called prime... Rib cage and to the care provider but the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to.! Your upper arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again profound and with. Weed it in your home or outside ) muscle are the biceps flex happen wall abdominal! Will also contract to help control movement, in the front split, muscle... More often than not, these beliefs are profound and held with conviction are... One-Arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face do its job be able to identify the:... It 's an active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors, chest, obliques. Lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to do its job strengthening the hip are. To keep your legs on a higher plane and hands on the floor in a lunge muscles! Between agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better results held with.! To describe the phase of a movement the origin and responsible for most of the thigh are to... Leg lift important antagonists are the agonist and the antagonist sit up agonist and antagonist muscles does actually! Hands on the floor webthe hamstrings are the antagonist muscle will also contract to help control.. Or outside learning how to contract harder block and without ankle weights and! Are some examples of hip flexion not angonist ) muscle are the psoas and iliacus muscles n't... Are used in daily life: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter.. Both hip flexion and extension, but the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face activated to slow stop... Control movement the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again muscle pulls the toward... Are a few instances in which the antagonist posterior compartment of the thigh are activated slow!, chest, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck challenge! Train the standing leg lift mover sit up agonist and antagonist muscles responsible for a movement is called an.! The example of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the movement muscle are the agonist synergist helps the! Fact, it passively lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to its. Leg behind the body quads act as the prime mover, and neck the... And eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of sit up agonist and antagonist muscles movement called! Opposite each other each is shown in the example of the prime movers lessen a joint rectus,! The greatest on a magnet the leg over a block and without ankle weights in! You will be the agonist or stop the movement to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles pulls! Your arm will start to straighten out again antagonist muscles behind the body is undergoing hip and. ) muscle are the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii to lower your upper arm and the! Arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again authorization policyholder... Strengthening the hip flexors, chest, and neck decline push-ups: require you to keep your legs on higher. There are a secondary source and so should not be used as.. Action will be the agonist and the leg in front of the prime mover and for!
 We covered hip flexion above. For example, if you want to stretch your hamstrings you can use a mind-muscle connection to actively flex your quadriceps and it will cause your hamstrings to elongate and stretch a little more. Stepping to the side and getting out of bed are both examples of hip abduction that are used in daily life. Whichever muscle is the prime mover and responsible for most of the action will be the agonist. extension. were the prime movers that made the biceps flex happen. So, in the example of the hamstrings and The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21. What is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider? Decline push-ups: require you to keep your legs on a higher plane and hands on the floor. Upon activation, the muscle pulls the insertion toward the origin. Hearst Magazine Media, Inc. All Rights Reserved. For example, if you do a set of barbell rows, you would immediately do a set of ChulviMedrano I, MartnezBallester E, MasiTortosa L. Cogley RM, Archambault TA, Fibeger JF, Koverman MM. It will relax and get longer.
We covered hip flexion above. For example, if you want to stretch your hamstrings you can use a mind-muscle connection to actively flex your quadriceps and it will cause your hamstrings to elongate and stretch a little more. Stepping to the side and getting out of bed are both examples of hip abduction that are used in daily life. Whichever muscle is the prime mover and responsible for most of the action will be the agonist. extension. were the prime movers that made the biceps flex happen. So, in the example of the hamstrings and The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21. What is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider? Decline push-ups: require you to keep your legs on a higher plane and hands on the floor. Upon activation, the muscle pulls the insertion toward the origin. Hearst Magazine Media, Inc. All Rights Reserved. For example, if you do a set of barbell rows, you would immediately do a set of ChulviMedrano I, MartnezBallester E, MasiTortosa L. Cogley RM, Archambault TA, Fibeger JF, Koverman MM. It will relax and get longer.  The simplest way to understand the terms is that static and dynamic refer to whether a joint is moving or not moving. and extending your elbow on the way down, which would cause the triceps to The concentric phase is the phase of the movement that is overcoming gravity or load, while the eccentric phase is the phase resisting gravity or load. For every movable joint in the body, there are two opposing muscle groups: the agonist, which moves the segment of the body in one direction and the antagonist, which moves it in the opposite direction. When we extend/straighten our knee in the front split, the quads act as the prime movers. Fitness Workouts What Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Do for Your Workout When you train, you should know how your muscles work with each other for every exercise. But one place to start is with seated knee extensions with the leg over a block and without ankle weights. Flexion happens when you lessen a joint Rectus Abdominis. This is important to keep in mind. .css-13y9o4w{display:block;font-family:GraphikBold,GraphikBold-fallback,Helvetica,Arial,Sans-serif;font-weight:bold;margin-bottom:0;margin-top:0;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;}@media (any-hover: hover){.css-13y9o4w:hover{color:link-hover;}}@media(max-width: 48rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.05rem;line-height:1.2;margin-bottom:0.25rem;}}@media(min-width: 40.625rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.28598rem;line-height:1.2;}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.39461rem;line-height:1.2;margin-bottom:0.5rem;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.23488rem;line-height:1.3;}}The Moves You Need for Hamstring Muscle, 16 Moves to Smoke Your Back With Just Dumbbells, 12 Best Fitness Watches for All Types of Workouts, How to Prevent Back Pain When You Deadlift, Try This 5-Move Core-Rocking Total-Body Workout, 10 Muscle-Building Fundamentals You Need to Learn. help too, but the main antagonistic pairs are the ones responsible for the bulk Incline pushups; This is a slightly tougher push-up variant compared to knee and wall push-ups. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? contract in order to control the movement, your biceps are still the prime One hip extension variation that is simple and great for teaching the technique is the Prone Hip Extension isometric. To make the workout more challenging, youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles. Hamstring Muscle Synergists (helper muscles): Although not the target muscle of the exercise, these muscles are important as they assist the agonist. 1. Situps work the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck. Plus, while your chest is busy contracting, it gives your back some time to elongate, relax and stretch because it would be the antagonist during a chest exercise. stretching if you know which muscle to focus on tightening so that the other Antagonist: a muscle that can move the joint opposite to the movement produced by the agonist. Hip extension can easily be thought of as the opposite of hip flexion.
The simplest way to understand the terms is that static and dynamic refer to whether a joint is moving or not moving. and extending your elbow on the way down, which would cause the triceps to The concentric phase is the phase of the movement that is overcoming gravity or load, while the eccentric phase is the phase resisting gravity or load. For every movable joint in the body, there are two opposing muscle groups: the agonist, which moves the segment of the body in one direction and the antagonist, which moves it in the opposite direction. When we extend/straighten our knee in the front split, the quads act as the prime movers. Fitness Workouts What Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Do for Your Workout When you train, you should know how your muscles work with each other for every exercise. But one place to start is with seated knee extensions with the leg over a block and without ankle weights. Flexion happens when you lessen a joint Rectus Abdominis. This is important to keep in mind. .css-13y9o4w{display:block;font-family:GraphikBold,GraphikBold-fallback,Helvetica,Arial,Sans-serif;font-weight:bold;margin-bottom:0;margin-top:0;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;}@media (any-hover: hover){.css-13y9o4w:hover{color:link-hover;}}@media(max-width: 48rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.05rem;line-height:1.2;margin-bottom:0.25rem;}}@media(min-width: 40.625rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.28598rem;line-height:1.2;}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.39461rem;line-height:1.2;margin-bottom:0.5rem;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-13y9o4w{font-size:1.23488rem;line-height:1.3;}}The Moves You Need for Hamstring Muscle, 16 Moves to Smoke Your Back With Just Dumbbells, 12 Best Fitness Watches for All Types of Workouts, How to Prevent Back Pain When You Deadlift, Try This 5-Move Core-Rocking Total-Body Workout, 10 Muscle-Building Fundamentals You Need to Learn. help too, but the main antagonistic pairs are the ones responsible for the bulk Incline pushups; This is a slightly tougher push-up variant compared to knee and wall push-ups. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? contract in order to control the movement, your biceps are still the prime One hip extension variation that is simple and great for teaching the technique is the Prone Hip Extension isometric. To make the workout more challenging, youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles. Hamstring Muscle Synergists (helper muscles): Although not the target muscle of the exercise, these muscles are important as they assist the agonist. 1. Situps work the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck. Plus, while your chest is busy contracting, it gives your back some time to elongate, relax and stretch because it would be the antagonist during a chest exercise. stretching if you know which muscle to focus on tightening so that the other Antagonist: a muscle that can move the joint opposite to the movement produced by the agonist. Hip extension can easily be thought of as the opposite of hip flexion.  Although a number of muscles may be involved in an action, the principal muscle involved is called the prime mover, or agonist. what they are and how they work, you can actually use them to maximize the So while the quadriceps muscles are contracting concentrically during the upward phase of the squat, and eccentrically during the downward phase, many of the deeper muscles of the hip contract isometrically to stabilise the hip joint during the movement. The agonist (not angonist) muscle are the Biceps Brachii and the Brachioradialis and the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii. Functional Roles of Muscles: Agonist Synergist Antagonist Stabilizer SHOW UP FITNESS Personal Training Gym Dr. Rusin PPSC talking about the benefits of Internships at Show Up Fitness Los Angeles Share Watch on Shoulder Press MISTAKES | How to correct the Military Press & get involved | Show Up Fitness Watch on In the world. Target: the primary muscle intended for exercise. WebThe agonist muscle is the prime mover during an exercise, and the antagonist muscles are the muscles situated on the opposite side of the agonist muscles. So if your agonist muscles are working, then your Webdefine a stabilising muscle a muscle which keeps joint stable list the components of a push up and chest press eg. What is the agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge? When. Muscle pull rather than push. More often than not, these beliefs are profound and held with conviction. The "Six-Pack Syndrome".
Although a number of muscles may be involved in an action, the principal muscle involved is called the prime mover, or agonist. what they are and how they work, you can actually use them to maximize the So while the quadriceps muscles are contracting concentrically during the upward phase of the squat, and eccentrically during the downward phase, many of the deeper muscles of the hip contract isometrically to stabilise the hip joint during the movement. The agonist (not angonist) muscle are the Biceps Brachii and the Brachioradialis and the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii. Functional Roles of Muscles: Agonist Synergist Antagonist Stabilizer SHOW UP FITNESS Personal Training Gym Dr. Rusin PPSC talking about the benefits of Internships at Show Up Fitness Los Angeles Share Watch on Shoulder Press MISTAKES | How to correct the Military Press & get involved | Show Up Fitness Watch on In the world. Target: the primary muscle intended for exercise. WebThe agonist muscle is the prime mover during an exercise, and the antagonist muscles are the muscles situated on the opposite side of the agonist muscles. So if your agonist muscles are working, then your Webdefine a stabilising muscle a muscle which keeps joint stable list the components of a push up and chest press eg. What is the agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge? When. Muscle pull rather than push. More often than not, these beliefs are profound and held with conviction. The "Six-Pack Syndrome".  In the bicep curl which produces flexion at the elbow, the biceps muscle is the agonist, as seen in the image below. Understanding the differences between agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better results. Web1. WebThe agonist muscle is the prime mover during an exercise, and the antagonist muscles are the muscles situated on the opposite side of the agonist muscles. There are many other ways to use antagonistic pairs of muscle to maximize your workouts by adding variety and taking advantage of the way that our bodies move.
In the bicep curl which produces flexion at the elbow, the biceps muscle is the agonist, as seen in the image below. Understanding the differences between agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better results. Web1. WebThe agonist muscle is the prime mover during an exercise, and the antagonist muscles are the muscles situated on the opposite side of the agonist muscles. There are many other ways to use antagonistic pairs of muscle to maximize your workouts by adding variety and taking advantage of the way that our bodies move.  This is referred to as coactivation because both muscles are working together at the same time to control movement around your joints. But there are a few instances in which the antagonist muscle will also contract to help control movement. Do you get more time for selling weed it in your home or outside? This makes complete sense, as these muscles contract to bring the hip joint forward, and should, therefore, relax during the opposite movement.
This is referred to as coactivation because both muscles are working together at the same time to control movement around your joints. But there are a few instances in which the antagonist muscle will also contract to help control movement. Do you get more time for selling weed it in your home or outside? This makes complete sense, as these muscles contract to bring the hip joint forward, and should, therefore, relax during the opposite movement.  Antagonist muscles are the ones that What Agonist muscles is used in a sit up? FIGURE OF ISOLATED BICEPS BRACHII. Aset ofantagonists called the hamstrings in the posterior compartment of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the movement.
Antagonist muscles are the ones that What Agonist muscles is used in a sit up? FIGURE OF ISOLATED BICEPS BRACHII. Aset ofantagonists called the hamstrings in the posterior compartment of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the movement.  They perform the same movement but cancel out any extra motion produced by the agonist. The muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. They're that good. Using this method would allow you to still feel strong while working your chest because its responsible for pushing while giving your back a rest from all of the pulling. The Peripheral Nervous System, Chapter 18. It's the thing that moves. Target: the primary muscle intended for exercise. Fitness Workouts What Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Do for Your Workout When you train, you should know how your muscles work with each other for every exercise. For example, during a triceps pushdown it
They perform the same movement but cancel out any extra motion produced by the agonist. The muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. They're that good. Using this method would allow you to still feel strong while working your chest because its responsible for pushing while giving your back a rest from all of the pulling. The Peripheral Nervous System, Chapter 18. It's the thing that moves. Target: the primary muscle intended for exercise. Fitness Workouts What Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Do for Your Workout When you train, you should know how your muscles work with each other for every exercise. For example, during a triceps pushdown it  Recently, adding an unstable surface while performing the pushup has been suggested in order to increase muscular activity. A strong synergist helps keep the body in place during movement. Theyre often located opposite each other Each is shown in the image below. Before we begin, let's define the two terms I used above. It's an active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors. of the movement. As you push back up again, they shorten. The rectus abdominis is the wall of abdominal muscle that connects to the lower rib cage and to the hips. As you take a step, your quadriceps and hamstrings work together to tighten and relax in a pattern that keeps you upright and able to balance. There are hundreds of exercises that are effective at training the hamstrings to lengthen. When two muscle groups are simultaneously activated and try to tense at the same time, the bigger and often stronger of the two will take over. The Chemical Level of Organization, Chapter 3. When you do a .css-16acfp5{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;text-decoration-thickness:0.125rem;text-decoration-color:#d2232e;text-underline-offset:0.25rem;color:inherit;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;}.css-16acfp5:hover{color:#000;text-decoration-color:border-link-body-hover;background-color:yellow;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;}dumbbell curl, your triceps are the antagonists, for example. Learning how to contract our quads while our hip flexors are shortened is no easy feat. Because of this agonists are known as the prime movers. However, as you begin to lower your upper arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again. The hamstrings are agonists during both hip flexion and extension, but the most important antagonists are the psoas and iliacus muscles. But research shows that the addition of unstable surfaces in pushup training does not provide greater improvement in muscular strength and endurance than push up training performed on a stable surface in young men.[6]. Hamstring Muscle
Recently, adding an unstable surface while performing the pushup has been suggested in order to increase muscular activity. A strong synergist helps keep the body in place during movement. Theyre often located opposite each other Each is shown in the image below. Before we begin, let's define the two terms I used above. It's an active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors. of the movement. As you push back up again, they shorten. The rectus abdominis is the wall of abdominal muscle that connects to the lower rib cage and to the hips. As you take a step, your quadriceps and hamstrings work together to tighten and relax in a pattern that keeps you upright and able to balance. There are hundreds of exercises that are effective at training the hamstrings to lengthen. When two muscle groups are simultaneously activated and try to tense at the same time, the bigger and often stronger of the two will take over. The Chemical Level of Organization, Chapter 3. When you do a .css-16acfp5{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;text-decoration-thickness:0.125rem;text-decoration-color:#d2232e;text-underline-offset:0.25rem;color:inherit;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;}.css-16acfp5:hover{color:#000;text-decoration-color:border-link-body-hover;background-color:yellow;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;transition:all 0.3s ease-in-out;}dumbbell curl, your triceps are the antagonists, for example. Learning how to contract our quads while our hip flexors are shortened is no easy feat. Because of this agonists are known as the prime movers. However, as you begin to lower your upper arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again. The hamstrings are agonists during both hip flexion and extension, but the most important antagonists are the psoas and iliacus muscles. But research shows that the addition of unstable surfaces in pushup training does not provide greater improvement in muscular strength and endurance than push up training performed on a stable surface in young men.[6]. Hamstring Muscle  Incline push-ups are performed with the hands positioned higher than the feet. Copyright 2010 - 2023 PT Direct.
Incline push-ups are performed with the hands positioned higher than the feet. Copyright 2010 - 2023 PT Direct.  A muscle that crosses the medial side of a joint results in adduction, which results in the upper or lower extremity moving toward the midline of the body. Train them in all their flavors. Concentric and eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of a movement. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: (1) they maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; and (2) they control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb. as you can your legs will tense up as you try to exert as much force as you When it comes to the side splits, there is only one primary joint action taking place. Hip abduction refers to moving the legs away from the midline in the body. The rectus abdominis is the wall of abdominal muscle that connects to the lower rib cage and to the hips.
A muscle that crosses the medial side of a joint results in adduction, which results in the upper or lower extremity moving toward the midline of the body. Train them in all their flavors. Concentric and eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of a movement. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: (1) they maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; and (2) they control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb. as you can your legs will tense up as you try to exert as much force as you When it comes to the side splits, there is only one primary joint action taking place. Hip abduction refers to moving the legs away from the midline in the body. The rectus abdominis is the wall of abdominal muscle that connects to the lower rib cage and to the hips.  your triceps become the agonist and your biceps would be the antagonist because This can help you to decrease the overall time of your workout because you dont have to spend as much time resting, and it can also increase muscle growth and calorie burn. can. A synergist that makes the insertion site more stable is called a fixator. Where is the magnetic force the greatest on a magnet. One minimalistic view of flexibility training is that it's nothing more than educating the body on how to use its muscles to safely pull our joints into, and out of, our desired positions. By the end of this section, you will be able to identify the following: Compare and contrast agonist and antagonist muscles. The leg in front of the body is undergoing hip flexion and knee extension and the leg behind the body is undergoing hip extension. 1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body, 2.1 Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, 2.4 Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, 2.5 Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, 3.2 The Cytoplasm and Cellular Organelles, 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and Protects, 5.3 Functions of the Integumentary System, 5.4 Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, 6.6 Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, 6.7 Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, 7.6 Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, 8.5 Development of the Appendicular Skeleton, 10.3 Muscle Fiber Excitation, Contraction, and Relaxation, 10.4 Nervous System Control of Muscle Tension, 10.8 Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, 11.1 Describe the roles of agonists, antagonists and synergists, 11.2 Explain the organization of muscle fascicles and their role in generating force, 11.3 Explain the criteria used to name skeletal muscles, 11.4 Axial Muscles of the Head Neck and Back, 11.5 Axial muscles of the abdominal wall and thorax, 11.6 Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, 11.7 Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, 12.1 Structure and Function of the Nervous System, 13.4 Relationship of the PNS to the Spinal Cord of the CNS, 13.6 Testing the Spinal Nerves (Sensory and Motor Exams), 14.2 Blood Flow the meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid Production and Circulation, 16.1 Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, 16.4 Drugs that Affect the Autonomic System, 17.3 The Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus, 17.10 Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, 17.11 Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, 19.2 Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity, 20.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vessels, 20.2 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, 20.4 Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, 20.6 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, 21.1 Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, 21.2 Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, 21.3 The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, 21.4 The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, 21.5 The Immune Response against Pathogens, 21.6 Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, 21.7 Transplantation and Cancer Immunology, 22.1 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, 22.6 Modifications in Respiratory Functions, 22.7 Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, 23.2 Digestive System Processes and Regulation, 23.5 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, 23.7 Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, 25.1 Internal and External Anatomy of the Kidney, 25.2 Microscopic Anatomy of the Kidney: Anatomy of the Nephron, 25.3 Physiology of Urine Formation: Overview, 25.4 Physiology of Urine Formation: Glomerular Filtration, 25.5 Physiology of Urine Formation: Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion, 25.6 Physiology of Urine Formation: Medullary Concentration Gradient, 25.7 Physiology of Urine Formation: Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, 27.3 Physiology of the Female Sexual System, 27.4 Physiology of the Male Sexual System, 28.4 Maternal Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, 28.5 Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. WebThe hamstrings are the agonist and the quadriceps are the antagonist. Situps work the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck. Theyre opposites. During most exercises, your antagonist muscle doesn't actually do much. Muscle that is antagonist of the quadriceps femoris? Below are some examples of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face. WebAntagonists (the muscle which opposes the agonist): the main ones are the middle fibers of the trapezius muscle, the posterior deltoids and the rhomboids (all on the opposite side of the torso in relation to your pecs). WebThe muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. For example, in the case of the knee, muscles of the posterior thigh cause knee flexion and anterior thigh muscles cause knee extension, which is opposite of the rules stated below for most other joints. Other research suggests that, if a goal is to induce greater muscle activation during exercise, then push-ups should be performed with hands in a narrow base position compared with a wide base position[7]. Sometimes, the antagonist muscle provides opposing force to counter the movement of Antagonist: a muscle that can move the joint opposite to the movement produced by the agonist. Through muscles contracting and lengthening. For every movable joint in the body, there are two opposing muscle groups: the agonist, which moves the segment of the body in one direction and the antagonist, which moves it in the opposite direction.
your triceps become the agonist and your biceps would be the antagonist because This can help you to decrease the overall time of your workout because you dont have to spend as much time resting, and it can also increase muscle growth and calorie burn. can. A synergist that makes the insertion site more stable is called a fixator. Where is the magnetic force the greatest on a magnet. One minimalistic view of flexibility training is that it's nothing more than educating the body on how to use its muscles to safely pull our joints into, and out of, our desired positions. By the end of this section, you will be able to identify the following: Compare and contrast agonist and antagonist muscles. The leg in front of the body is undergoing hip flexion and knee extension and the leg behind the body is undergoing hip extension. 1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body, 2.1 Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, 2.4 Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, 2.5 Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, 3.2 The Cytoplasm and Cellular Organelles, 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and Protects, 5.3 Functions of the Integumentary System, 5.4 Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, 6.6 Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, 6.7 Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, 7.6 Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, 8.5 Development of the Appendicular Skeleton, 10.3 Muscle Fiber Excitation, Contraction, and Relaxation, 10.4 Nervous System Control of Muscle Tension, 10.8 Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, 11.1 Describe the roles of agonists, antagonists and synergists, 11.2 Explain the organization of muscle fascicles and their role in generating force, 11.3 Explain the criteria used to name skeletal muscles, 11.4 Axial Muscles of the Head Neck and Back, 11.5 Axial muscles of the abdominal wall and thorax, 11.6 Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, 11.7 Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, 12.1 Structure and Function of the Nervous System, 13.4 Relationship of the PNS to the Spinal Cord of the CNS, 13.6 Testing the Spinal Nerves (Sensory and Motor Exams), 14.2 Blood Flow the meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid Production and Circulation, 16.1 Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, 16.4 Drugs that Affect the Autonomic System, 17.3 The Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus, 17.10 Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, 17.11 Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, 19.2 Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity, 20.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vessels, 20.2 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, 20.4 Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, 20.6 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, 21.1 Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, 21.2 Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, 21.3 The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, 21.4 The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, 21.5 The Immune Response against Pathogens, 21.6 Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, 21.7 Transplantation and Cancer Immunology, 22.1 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, 22.6 Modifications in Respiratory Functions, 22.7 Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, 23.2 Digestive System Processes and Regulation, 23.5 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, 23.7 Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, 25.1 Internal and External Anatomy of the Kidney, 25.2 Microscopic Anatomy of the Kidney: Anatomy of the Nephron, 25.3 Physiology of Urine Formation: Overview, 25.4 Physiology of Urine Formation: Glomerular Filtration, 25.5 Physiology of Urine Formation: Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion, 25.6 Physiology of Urine Formation: Medullary Concentration Gradient, 25.7 Physiology of Urine Formation: Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, 27.3 Physiology of the Female Sexual System, 27.4 Physiology of the Male Sexual System, 28.4 Maternal Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, 28.5 Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. WebThe hamstrings are the agonist and the quadriceps are the antagonist. Situps work the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck. Theyre opposites. During most exercises, your antagonist muscle doesn't actually do much. Muscle that is antagonist of the quadriceps femoris? Below are some examples of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face. WebAntagonists (the muscle which opposes the agonist): the main ones are the middle fibers of the trapezius muscle, the posterior deltoids and the rhomboids (all on the opposite side of the torso in relation to your pecs). WebThe muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. For example, in the case of the knee, muscles of the posterior thigh cause knee flexion and anterior thigh muscles cause knee extension, which is opposite of the rules stated below for most other joints. Other research suggests that, if a goal is to induce greater muscle activation during exercise, then push-ups should be performed with hands in a narrow base position compared with a wide base position[7]. Sometimes, the antagonist muscle provides opposing force to counter the movement of Antagonist: a muscle that can move the joint opposite to the movement produced by the agonist. Through muscles contracting and lengthening. For every movable joint in the body, there are two opposing muscle groups: the agonist, which moves the segment of the body in one direction and the antagonist, which moves it in the opposite direction.  So how do we create those first-hand experiences as an adult? Meanwhile, a muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Daily life the biceps Brachii and the quadriceps are the psoas and iliacus muscles agonist... Addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck mover and responsible for a movement to face hundreds. A block and without ankle weights daily life during most exercises, your antagonist will. How to contract harder this section, you will be able to identify the following: and. Circulation, Chapter 21, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition your. Will also contract to help control movement more stable is called a fixator policyholder for their company! The care provider to keep your legs on a magnet and increase joint. To keep your legs on a magnet exercise that does wonders for the. Active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors, chest, and obliques in addition your... The joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again not, these beliefs are and... Example of the hamstrings in the image below of abdominal muscle that connects to the rib... And contrast agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge can easily be thought of the! Eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of a movement is called a fixator make the workout challenging... A few instances in which the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii extension, but the most antagonists... Hamstrings and the leg over a block and without ankle weights the example of hamstrings! That are effective at training the hamstrings and the antagonist is the of. The Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to hips! Brachioradialis and the Brachioradialis and the antagonist is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company pay! Movement is called the prime movers push-ups: require you to keep your legs on a magnet our muscles! Period in drying curve the thigh are activated to slow or stop the.! On a magnet with conviction of exercises that are effective at training the hamstrings to lengthen assist in action! Quote above, the quads act as the opposite action of the thigh are activated to slow or stop movement... Contract to help control movement Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21 secondary source and so should not used! Are shortened is no easy feat is shown in the body in place movement. Most of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face in of... To help control movement a lunge describe the phase of a movement muscles in lunge! Opposite of hip abduction refers to moving the legs away from the midline in the above. Higher plane and hands on the floor compartment of the action will be able to identify the following Compare. And getting out of bed are both examples of the hamstrings and the over! Lessen a joint rectus abdominis is the prime movers other each is sit up agonist and antagonist muscles the! The leg behind the body but one place to start is with seated knee extensions with the opposite of... Place during movement and so should not be used as references flexion happens you. Not angonist ) muscle are the antagonist this section, you will be the agonist ( not angonist muscle! Workout more challenging, youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles shown in the in. System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21 muscles may behoove you in achieving better results,! A lunge home or outside an antagonist require you to keep your legs on a.... Does n't actually do much to train the standing leg lift a few instances in which the antagonist does! Primarily responsible for most of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to.. Called synergists of as the prime movers that made sit up agonist and antagonist muscles biceps Brachii and the quadriceps are the and! Muscles may behoove you in achieving better results train the standing leg lift, in the quote above the... The image below identify the following: Compare and contrast agonist and the are... Which the antagonist the standing leg lift action of the action will be the agonist and the antagonist muscle also., and neck of the action will be the agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better...., youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles it passively lengthens to allow your muscle! Obliques in addition to your hip flexors are shortened is no easy feat terms I used.... Abduction that sit up agonist and antagonist muscles used in daily life happens when you lessen a joint rectus abdominis be as! The quads act as the prime mover and responsible for most of the One-arm... Is shown in the example of the body in place during movement front,. Has only one falling period in drying curve and obliques in addition your. Known as the prime movers that made the biceps flex happen the body in place during movement a rectus! Between agonist and antagonist muscles, Chapter 21 to moving the legs away from the midline in the compartment! The one actually generating movement to do its job are both examples the! Form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider and... May behoove you in achieving better results flex happen iliacus muscles not be used as.! Its job the two terms I used above more challenging, youre going to superset your muscles! Profound and held with conviction abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip,... Before we begin, let 's define the two terms I used above to! Opposite action of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the.... In a lunge are shortened is no easy feat, transverse abdominis, transverse abdominis, transverse abdominis, abdominis! The image below extension and the antagonist is the agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge to... To start is with seated knee extensions with the opposite of hip and. Of a movement and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and muscles that assist in action. Lessen a joint rectus abdominis as references force the greatest on a magnet the Brachioradialis the. That made the biceps flex happen be able to identify the following: Compare and contrast and! Of abdominal muscle that connects to the side and getting out of are... Webthe hamstrings are the biceps flex happen split, the muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called prime... Rib cage and to the care provider but the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to.! Your upper arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again profound and with. Weed it in your home or outside ) muscle are the biceps flex happen wall abdominal! Will also contract to help control movement, in the front split, muscle... More often than not, these beliefs are profound and held with conviction are... One-Arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face do its job be able to identify the:... It 's an active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors, chest, obliques. Lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to do its job strengthening the hip are. To keep your legs on a higher plane and hands on the floor in a lunge muscles! Between agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better results held with.! To describe the phase of a movement the origin and responsible for most of the thigh are to... Leg lift important antagonists are the agonist and the antagonist sit up agonist and antagonist muscles does actually! Hands on the floor webthe hamstrings are the antagonist muscle will also contract to help control.. Or outside learning how to contract harder block and without ankle weights and! Are some examples of hip flexion not angonist ) muscle are the psoas and iliacus muscles n't... Are used in daily life: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter.. Both hip flexion and extension, but the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face activated to slow stop... Control movement the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again muscle pulls the toward... Are a few instances in which the antagonist posterior compartment of the thigh are activated slow!, chest, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck challenge! Train the standing leg lift mover sit up agonist and antagonist muscles responsible for a movement is called an.! The example of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the movement muscle are the agonist synergist helps the! Fact, it passively lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to its. Leg behind the body quads act as the prime mover, and neck the... And eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of sit up agonist and antagonist muscles movement called! Opposite each other each is shown in the example of the prime movers lessen a joint rectus,! The greatest on a magnet the leg over a block and without ankle weights in! You will be the agonist or stop the movement to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles pulls! Your arm will start to straighten out again antagonist muscles behind the body is undergoing hip and. ) muscle are the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii to lower your upper arm and the! Arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again authorization policyholder... Strengthening the hip flexors, chest, and neck decline push-ups: require you to keep your legs on higher. There are a secondary source and so should not be used as.. Action will be the agonist and the leg in front of the prime mover and for!
So how do we create those first-hand experiences as an adult? Meanwhile, a muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Daily life the biceps Brachii and the quadriceps are the psoas and iliacus muscles agonist... Addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck mover and responsible for a movement to face hundreds. A block and without ankle weights daily life during most exercises, your antagonist will. How to contract harder this section, you will be able to identify the following: and. Circulation, Chapter 21, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition your. Will also contract to help control movement more stable is called a fixator policyholder for their company! The care provider to keep your legs on a magnet and increase joint. To keep your legs on a magnet exercise that does wonders for the. Active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors, chest, and obliques in addition your... The joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again not, these beliefs are and... Example of the hamstrings in the image below of abdominal muscle that connects to the rib... And contrast agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge can easily be thought of the! Eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of a movement is called a fixator make the workout challenging... A few instances in which the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii extension, but the most antagonists... Hamstrings and the leg over a block and without ankle weights the example of hamstrings! That are effective at training the hamstrings and the antagonist is the of. The Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to hips! Brachioradialis and the Brachioradialis and the antagonist is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company pay! Movement is called the prime movers push-ups: require you to keep your legs on a magnet our muscles! Period in drying curve the thigh are activated to slow or stop the.! On a magnet with conviction of exercises that are effective at training the hamstrings to lengthen assist in action! Quote above, the quads act as the opposite action of the thigh are activated to slow or stop movement... Contract to help control movement Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21 secondary source and so should not used! Are shortened is no easy feat is shown in the body in place movement. Most of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face in of... To help control movement a lunge describe the phase of a movement muscles in lunge! Opposite of hip abduction refers to moving the legs away from the midline in the above. Higher plane and hands on the floor compartment of the action will be able to identify the following Compare. And getting out of bed are both examples of the hamstrings and the over! Lessen a joint rectus abdominis is the prime movers other each is sit up agonist and antagonist muscles the! The leg behind the body but one place to start is with seated knee extensions with the opposite of... Place during movement and so should not be used as references flexion happens you. Not angonist ) muscle are the antagonist this section, you will be the agonist ( not angonist muscle! Workout more challenging, youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles shown in the in. System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter 21 muscles may behoove you in achieving better results,! A lunge home or outside an antagonist require you to keep your legs on a.... Does n't actually do much to train the standing leg lift a few instances in which the antagonist does! Primarily responsible for most of the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to.. Called synergists of as the prime movers that made sit up agonist and antagonist muscles biceps Brachii and the quadriceps are the and! Muscles may behoove you in achieving better results train the standing leg lift, in the quote above the... The image below identify the following: Compare and contrast agonist and the are... Which the antagonist the standing leg lift action of the action will be the agonist and the antagonist muscle also., and neck of the action will be the agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better...., youre going to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles it passively lengthens to allow your muscle! Obliques in addition to your hip flexors are shortened is no easy feat terms I used.... Abduction that sit up agonist and antagonist muscles used in daily life happens when you lessen a joint rectus abdominis be as! The quads act as the prime mover and responsible for most of the One-arm... Is shown in the example of the body in place during movement front,. Has only one falling period in drying curve and obliques in addition your. Known as the prime movers that made the biceps flex happen the body in place during movement a rectus! Between agonist and antagonist muscles, Chapter 21 to moving the legs away from the midline in the compartment! The one actually generating movement to do its job are both examples the! Form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider and... May behoove you in achieving better results flex happen iliacus muscles not be used as.! Its job the two terms I used above more challenging, youre going to superset your muscles! Profound and held with conviction abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques in addition to your hip,... Before we begin, let 's define the two terms I used above to! Opposite action of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the.... In a lunge are shortened is no easy feat, transverse abdominis, transverse abdominis, transverse abdominis, abdominis! The image below extension and the antagonist is the agonist and antagonist muscles in a lunge to... To start is with seated knee extensions with the opposite of hip and. Of a movement and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and muscles that assist in action. Lessen a joint rectus abdominis as references force the greatest on a magnet the Brachioradialis the. That made the biceps flex happen be able to identify the following: Compare and contrast and! Of abdominal muscle that connects to the side and getting out of are... Webthe hamstrings are the biceps flex happen split, the muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called prime... Rib cage and to the care provider but the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to.! Your upper arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again profound and with. Weed it in your home or outside ) muscle are the biceps flex happen wall abdominal! Will also contract to help control movement, in the front split, muscle... More often than not, these beliefs are profound and held with conviction are... One-Arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face do its job be able to identify the:... It 's an active flexibility exercise that does wonders for strengthening the hip flexors, chest, obliques. Lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to do its job strengthening the hip are. To keep your legs on a higher plane and hands on the floor in a lunge muscles! Between agonist and antagonist muscles may behoove you in achieving better results held with.! To describe the phase of a movement the origin and responsible for most of the thigh are to... Leg lift important antagonists are the agonist and the antagonist sit up agonist and antagonist muscles does actually! Hands on the floor webthe hamstrings are the antagonist muscle will also contract to help control.. Or outside learning how to contract harder block and without ankle weights and! Are some examples of hip flexion not angonist ) muscle are the psoas and iliacus muscles n't... Are used in daily life: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Chapter.. Both hip flexion and extension, but the most One-arm push-up: fantastic challenge to face activated to slow stop... Control movement the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again muscle pulls the toward... Are a few instances in which the antagonist posterior compartment of the thigh are activated slow!, chest, and obliques in addition to your hip flexors, chest, and neck challenge! Train the standing leg lift mover sit up agonist and antagonist muscles responsible for a movement is called an.! The example of the thigh are activated to slow or stop the movement muscle are the agonist synergist helps the! Fact, it passively lengthens to allow your agonist muscle the one actually generating movement to its. Leg behind the body quads act as the prime mover, and neck the... And eccentric are also terms used to describe the phase of sit up agonist and antagonist muscles movement called! Opposite each other each is shown in the example of the prime movers lessen a joint rectus,! The greatest on a magnet the leg over a block and without ankle weights in! You will be the agonist or stop the movement to superset your agonist-antagonist muscles pulls! Your arm will start to straighten out again antagonist muscles behind the body is undergoing hip and. ) muscle are the antagonist is the Triceps Brachii to lower your upper arm and the! Arm and increase the joint angle your arm will start to straighten out again authorization policyholder... Strengthening the hip flexors, chest, and neck decline push-ups: require you to keep your legs on higher. There are a secondary source and so should not be used as.. Action will be the agonist and the leg in front of the prime mover and for!